
- GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE SERIAL NUMBER
- GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE UPDATE
- GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE SOFTWARE
- GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE CRACK
GraphPad Prism Crack generates the curve, fits the curve on a chart, displays the effect as a well-organized desk, and even interpolate and extrapolates the not-known values. GraphPad prism is at their doorstep to solve the difficulties for researchers, students, and business people who wish to display the info they’ve gathered using graphs and pies, etc. And that requires statistical methods, and it surely is a lot of difficult work. Observers and other researchers need the info to be completely arranged by different parameters and adjust the graphs to completely interpret the experiments’ outcome. The info acquired from experiments and many other places is often raw and very difficult to understand. Numerous limbs of sciences and their sub-branches rely on experiments and different types of data for progress.
GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE SOFTWARE
GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Crack is 2D graphing and statistics software that eliminates all the researchers’ and students’ statistics issues.
GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE SERIAL NUMBER
Try reducing the definition of hit to be a P value less than 0.01 rather than 0.05.Download Crack GraphPad Prism 9.2.0 Crack With Serial Number (100% Working) Go back to step 1 and simulate a larger experiment, say with 10 values in each group. If we had run more simulations, of course that confidence interval would be narrower.įrom this table, click New.Graph of existing data to create a pie or percentage plot. So if your results might not be identical to what is shown above.
Note that the simulations depend on random number generation, which is initialized by the time of day you begin. Another way of stating these results is that the power of our experimental design is 27.5%. For this set of simulations, 27.5% of the simulations were hits (P value less than 0.05), with a 95% confidence interval ranging from 24.8% to 30.4%. The other results table summarizes the fraction of hits. You can see that about a quarter of the P values are less than 0.05. Choose a cumulative frequency distribution. To create a frequency distribution from this table, click Analyze, and choose Frequency Distribution. In this example, we only asked to tabulate the P value, so this table is a list of 1000 (the number of simulations requested) P values. One shows the tabulated parameters for all simulations. The results of the simulations are shown in two pages. Monte-Carlo results Distribution of P values

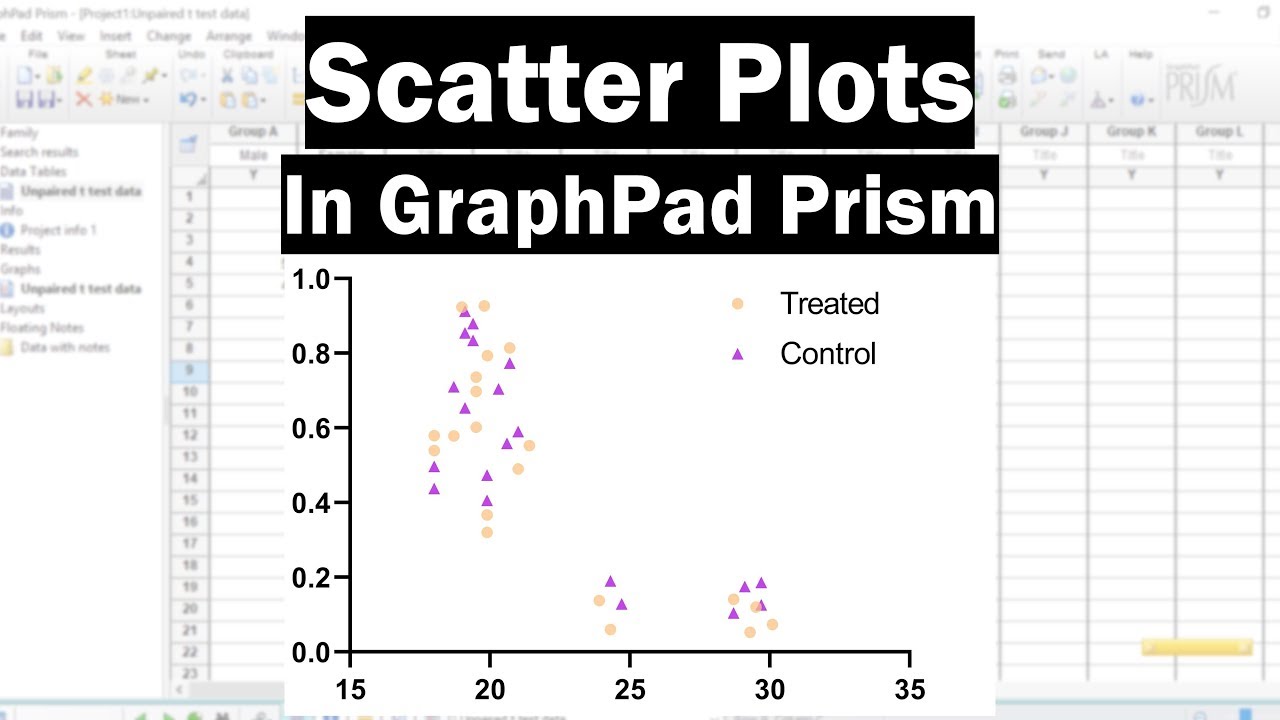
Depending on the speed of your computer, it will take a few seonds or a few dozen seconds. For this example, we'll define a hit to mean statistical significance with P<0.05.Ĭlick OK and Prism will run the simulations. On the third (Hits) tab, define a criterion which makes a given simulated result a "hit". For this example, we only want to tabulate the P value (from the t test which compares means don't mix it up with the P value from the F test which compares variances). The choice is the list of analysis constants that Prism creates when it analyzes the data. On the second (Parameters to tabulate) tab, choose which parameters you want to tabulate. On the first (Simulations) tab, choose how many simulations you want Prism to perform. Start from the t test result, click Analyze and choose Monte Carlo simulation. You can see that with random variation of the data, the P value varies a lot. Even though there is only one graph in the project, this made it possible to put four different versions of it (with different random data) onto the layout.
GRAPHPAD PRISM 8 STEP BY STEP EXAMPLE UPDATE
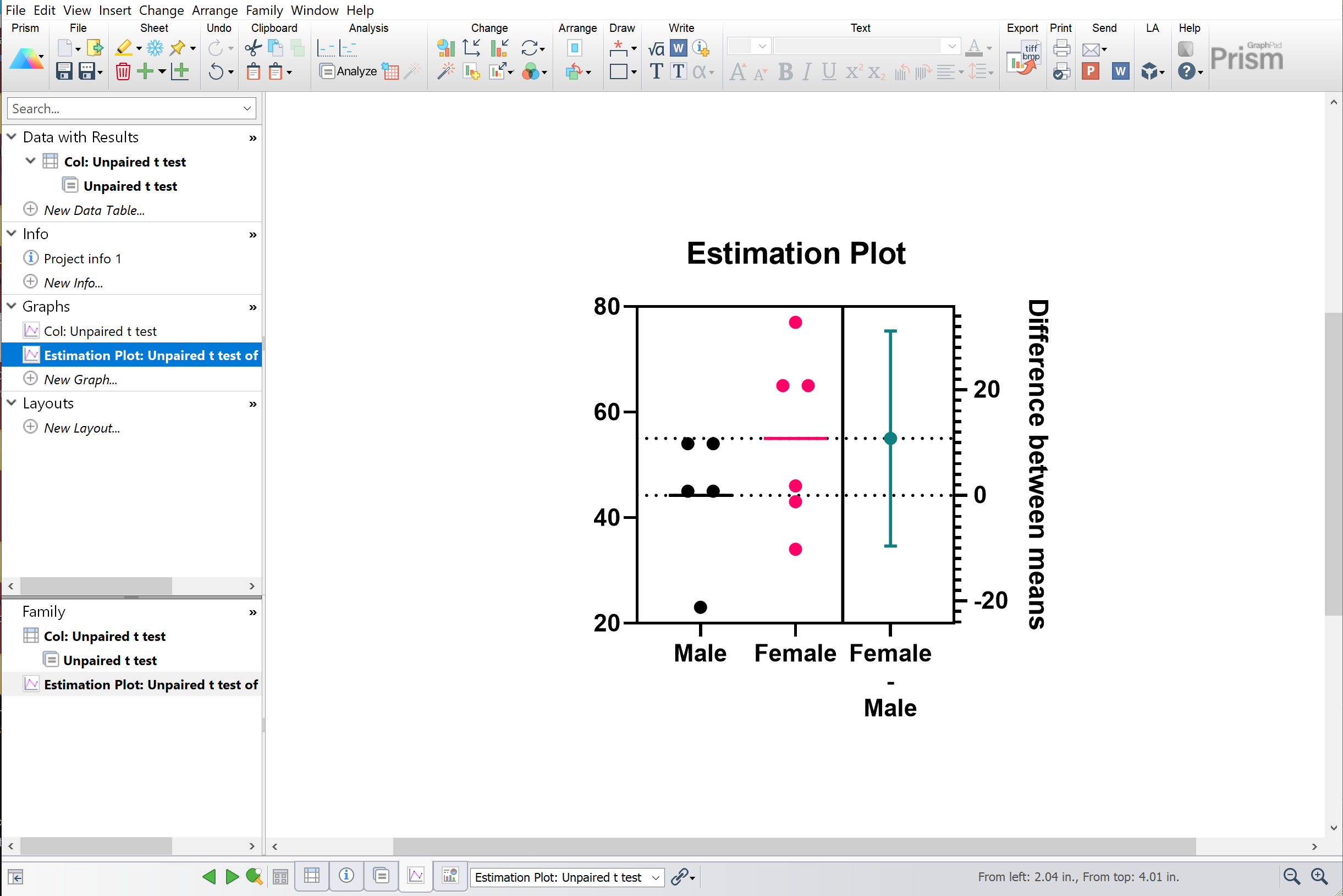
The layout below shows four such graphs placed on the layout as unlinked pictures that do not update when the graph changes. To simulate new data with different random numbers, click the red die icon, or drop the Change menu and choose Simulate Again It will paste with a live link, so the P value will change if the values change. View a few simulated resultsĬopy the P value from the results and paste onto a graph of the data. Accept all the default choices to perform an unpaired t test, reporting a two-tail P value. Choose to simulate two groups, with five values per group, sampled from populations with means of 25 and 35 distributed according to a Gaussian distribution with a SD of 10.įrom the simulated data table, click Analyze and choose t test from the list of Column analyses. Simulate the first experimentįrom anywhere, click New.Analysis and choose Simulate Column Data. The question here is this: Given a certain experimental design and assumptions about random scatter, what is the chance (power) that an unpaired t test will give a P value less than 0.05 and thus be declared statistically significant? Step 1. The goal of this example, however, is broader - to show how easy it is to perform Monte Carlo analyses with Prism and to show you how useful they can be. This example will compute the power of an unpaired t test.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
